Category: Lesson planning
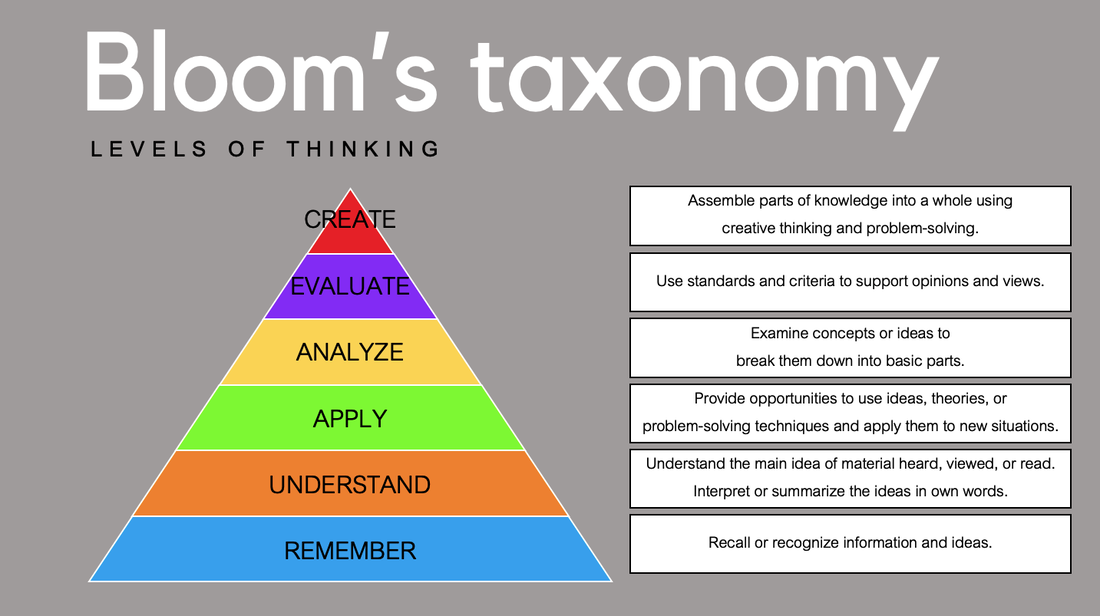
Bloom’s taxonomy was created in 1956 by Dr. Benjamin Bloom at the University of Chicago. It defines and distinguishes the level of human cognition. Bloom’s taxonomy divides thinking into six cognitive levels of complexity: remembering, understanding, applying, analyzing, evaluating and creating.
Purpose
The goals of an educator using Bloom's taxonomy are to:
The goals of an educator using Bloom's taxonomy are to:
- Encourage higher-order thought in his/her students by building up from lower-level cognitive skills.
- Promote the development of a new skill, knowledge or attitude.
- Discuss and exchange learning and assessment methods.
1. Remember
Action verbs
Arrange, define, describe, identify, label, list, match, memorize, name, order, recognize, recall, select and state.
Purpose of the level
Recall or recognize information and ideas.
Questions prompts
2. Understand
Actions verbs
Classify, compare, describe, discuss, distinguish, explain, give (examples), paraphrase, predict, recognize, summarize and translate.
Purpose of the level
Understand the main idea of material heard, viewed, or read. Interpret or summarize the ideas in own words.
Questions prompts
3. Apply
Actions verbs
Apply, change, choose, complete, demonstrate, dramatize, illustrate, interpret, modify, practice, produce, show, solve, use and write.
Purpose of the level
Provide opportunities to use ideas, theories, or problem-solving techniques and apply them to new situations.
Questions prompts
4. Analyze
Actions verbs
Analyze, calculate, categorize, contrast, discriminate, examine, infer, model and test.
Purpose of the level
Examine concepts or ideas to break them down into basic parts.
Questions prompts
5. Evaluate
Actions verbs
Argue, assess, conclude, criticize, debate, judge, justify, recommend, rate, support and evaluate.
Purpose of the level
Use standards and criteria to support opinions and views.
Questions prompts
6. Create
Actions verbs
Create, compose, construct, devise, design, generate, imagine, invent, plan, propose and write.
Purpose of the level
Assemble parts of knowledge into a whole using creative thinking and problem-solving.
Questions prompts
Action verbs
Arrange, define, describe, identify, label, list, match, memorize, name, order, recognize, recall, select and state.
Purpose of the level
Recall or recognize information and ideas.
Questions prompts
- What do you remember about…?
- What happened after...?
- Where is/are…?
- Who was/were…?
- When did…?
- What does it mean?
- How would you define…?
- Why did…?
- Which one…?
- How much…?
- How many…?
- Students name the main characters in the story.
- Students identify the irregular verbs in the paragraph.
- Students list the steps to use a blender.
- Students label the images.
- Students match the classic tales with the settings.
2. Understand
Actions verbs
Classify, compare, describe, discuss, distinguish, explain, give (examples), paraphrase, predict, recognize, summarize and translate.
Purpose of the level
Understand the main idea of material heard, viewed, or read. Interpret or summarize the ideas in own words.
Questions prompts
- Can you give an example of…?
- Can you choose the best definition of…?
- What would happen if…?
- Can you explain…?
- Can you read the graph?
- What could have happened next?
- Can you clarify…?
- Students describe the characters in the story.
- Students classify the list of words into nouns, verbs and adjectives.
- Students give examples of natural disasters.
- Students compare their answers with others.
- Students predict what the story may be about looking at the illustrations.
3. Apply
Actions verbs
Apply, change, choose, complete, demonstrate, dramatize, illustrate, interpret, modify, practice, produce, show, solve, use and write.
Purpose of the level
Provide opportunities to use ideas, theories, or problem-solving techniques and apply them to new situations.
Questions prompts
- Can you illustrate…?
- What factors would you change if…?
- Who do you think…?
- What was the main idea…?
- Why does… work?
- How would you solve…?
- Students illustrate the steps of the experiment.
- Students use the clues to complete the crossword puzzle.
- Students show a map of the city.
4. Analyze
Actions verbs
Analyze, calculate, categorize, contrast, discriminate, examine, infer, model and test.
Purpose of the level
Examine concepts or ideas to break them down into basic parts.
Questions prompts
- What’s the relationship between…?
- What’s the main idea of…?
- Which events could not have happened?
- How is … similar to …?
- What are some of the problems of …?
- Students infer the meaning of compound words.
- Students categorize facts included in an argument.
- Students calculate the circumference of a variety of wheels.
5. Evaluate
Actions verbs
Argue, assess, conclude, criticize, debate, judge, justify, recommend, rate, support and evaluate.
Purpose of the level
Use standards and criteria to support opinions and views.
Questions prompts
- What is the most important…?
- What would you suggest…?
- What criteria would you use to assess…?
- What data was used to evaluate…?
- What choice would you have made…?
- How would you determine the facts…?
- Students debate pros and cons of the death penalty.
- Students rate public services.
- Students recommend online resources for the topic.
6. Create
Actions verbs
Create, compose, construct, devise, design, generate, imagine, invent, plan, propose and write.
Purpose of the level
Assemble parts of knowledge into a whole using creative thinking and problem-solving.
Questions prompts
- What alternative would you suggest for…?
- What changes would you make to revise…?
- How would you generate a plan to…?
- What could you invent…?
- How would you improve…?
- Students design the human body chart.
- Students write their own autobiography.
- Students create a new character and explain how that character would fit into the storyline.
What to read next