Category: Teaching
Teaching vocabulary is very important in the language learning process. Indeed, it’s more important than grammar in communicative purposes, particularly in early stages. The linguist Wilkins argued that: “without grammar little can be conveyed, without vocabulary nothing can be conveyed”.
Teaching vocabulary plays an important role, if the students know or remember the meaning of the words, they will be able to understand what they hear and read, and they will express correctly when they speak or write.
Teaching vocabulary plays an important role, if the students know or remember the meaning of the words, they will be able to understand what they hear and read, and they will express correctly when they speak or write.
Memory triggers help student to remember the meaning of a word. These memory triggers could be:
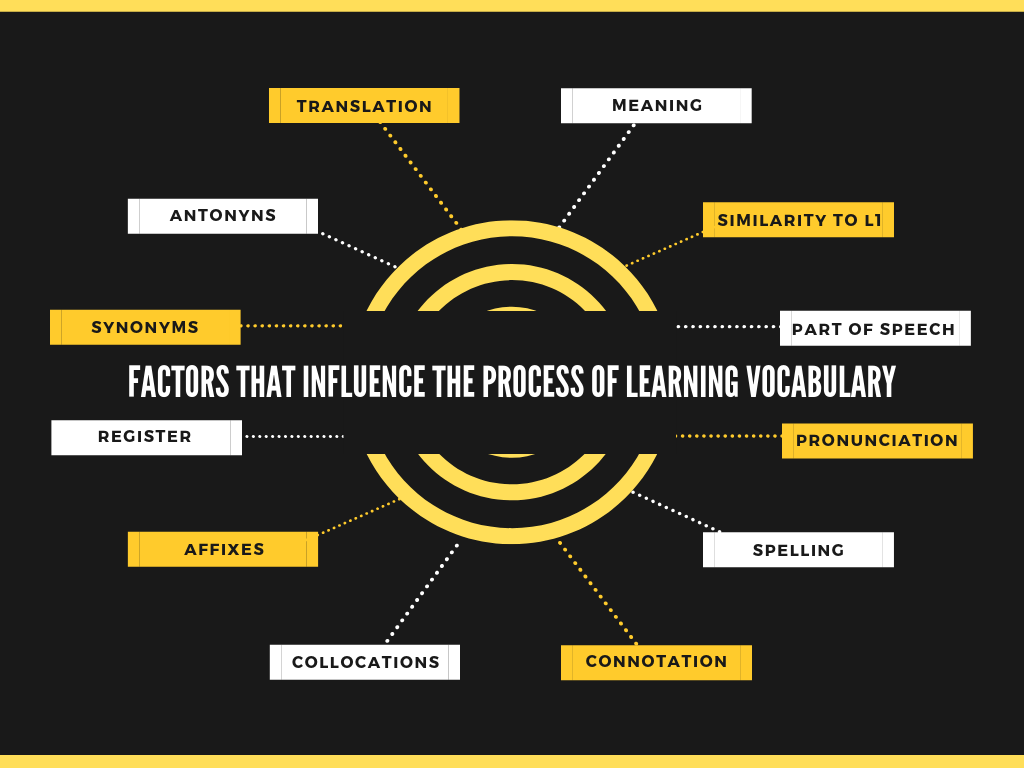
In English, like in any other foreign language, some words are easier to learn than others. However, it depends on many factors:
- A visual reminder such as a picture or diagram.
- The sound and rhythm of the word.
- The inclusion of the item in a sentence.
- The translation.
In English, like in any other foreign language, some words are easier to learn than others. However, it depends on many factors:
- Meaning.
- Similarity to L1.
- Similarity to English words you already know.
- Part of speech.
- Pronunciation.
- Spelling.
- Connotation (negative or positive).
- Collocations.
- Relation to others words (synonyms, antonyms and lexical sets).
- Affixes (prefixes and suffixes).
- Register (Formal, neutral and informal).
When we teach vocabulary, it's usual to introduce:
Ways to present vocabulary:
- The “easy” words before the “difficult” ones.
- The concrete before the abstract.
- The most frequent before the uncommon.
Ways to present vocabulary:
- Asking for the word translation in L1.
- Using visual aids (object, photographs, flashcards, and videos) of concrete words (pencil, city, big, etc.)
- Matching word-definition, word-illustration, word-pronunciation, etc.
- Miming action verbs.
- Using synonyms and antonyms.
- Contextualizing the meaning of the word giving examples.
- Using drilling activities.
- Using gapped example sentences.
- Categorizing words.